Imagine having the ability to check on your home automation, gather data from a garden sensor, or even manage a small server, all from miles away. That's a pretty cool thought, isn't it? The world of remote IoT, where tiny computers like the Raspberry Pi do big jobs, is truly fascinating. People are finding all sorts of clever ways to make these devices work for them, sometimes even trying to push the limits of what they can do.
Getting your Raspberry Pi to talk to you from a distance, securely and reliably, is a key part of these projects. It often means setting up special networks and using tools that keep your information safe. There are, for instance, a few ways to make sure your device is always within reach, even when you are not physically there. This kind of remote control opens up so many possibilities for hobbyists and creators alike, offering a lot of freedom in how you manage your smart setups.
This article will take a look at how to get your Raspberry Pi ready for remote access, focusing on secure methods like SSH within a Virtual Private Cloud (VPC) environment. We will also clear up some common questions, especially about whether you can really get a full Windows 10 experience on a Raspberry Pi, and what that might actually mean for your projects. It's about making sure your remote IoT plans are solid and well-informed, you know, so you can avoid headaches later.
Table of Contents
- Why Remote Access Matters for IoT Projects
- Setting Up Your Raspberry Pi for Remote Control
- Preparing the Raspberry Pi Hardware
- Getting Started with Raspberry Pi OS
- Understanding VPC and Its Role in Secure Remote IoT
- What is a Virtual Private Cloud (VPC)?
- Building a Secure Bridge with SSH
- Connecting to Your Raspberry Pi via SSH
- SSH Basics for Remote Pi Control
- Tips for SSH Security
- The Windows 10 Question: Raspberry Pi and Microsoft's OS
- Windows 10 IoT Core: A Different Story
- Running Full Windows 10: The Realities
- Alternative Approaches for Windows Users
- Practical Steps for a Remote IoT Setup
- Network Configuration Considerations
- Automating Remote Tasks
- Troubleshooting Common Remote Access Issues
- Frequently Asked Questions
Why Remote Access Matters for IoT Projects
Having remote access to your Internet of Things (IoT) devices, particularly something like a Raspberry Pi, is incredibly helpful. It means you can check on things, send commands, or even update software without having to be right next to the device. Think about a weather station in your backyard; you probably don't want to walk outside every time you need to see the data or make a small adjustment. That's where remote access comes in, offering a lot of convenience, you know.
For many people working on personal projects or even small-scale business solutions, the ability to control devices from anywhere is a big deal. It makes testing easier, allows for quick fixes if something goes wrong, and lets you collect information continuously. This kind of flexibility is quite valuable, especially when your devices are spread out or in hard-to-reach spots. It really changes how you can interact with your physical world through technology, actually.
Remote access also plays a very important role in security and maintenance. You can keep an eye on your devices for unusual activity, apply security updates promptly, and make sure everything is running smoothly. This proactive approach can prevent small problems from becoming much bigger ones. So, it's not just about convenience; it's also about keeping your IoT ecosystem healthy and safe, more or less.
Setting Up Your Raspberry Pi for Remote Control
Before you can control your Raspberry Pi from afar, you need to get it ready. This involves a few initial steps, making sure the hardware is correctly assembled and the right operating system is in place. It’s pretty straightforward, but it’s the foundation for everything else you’ll do, you know.
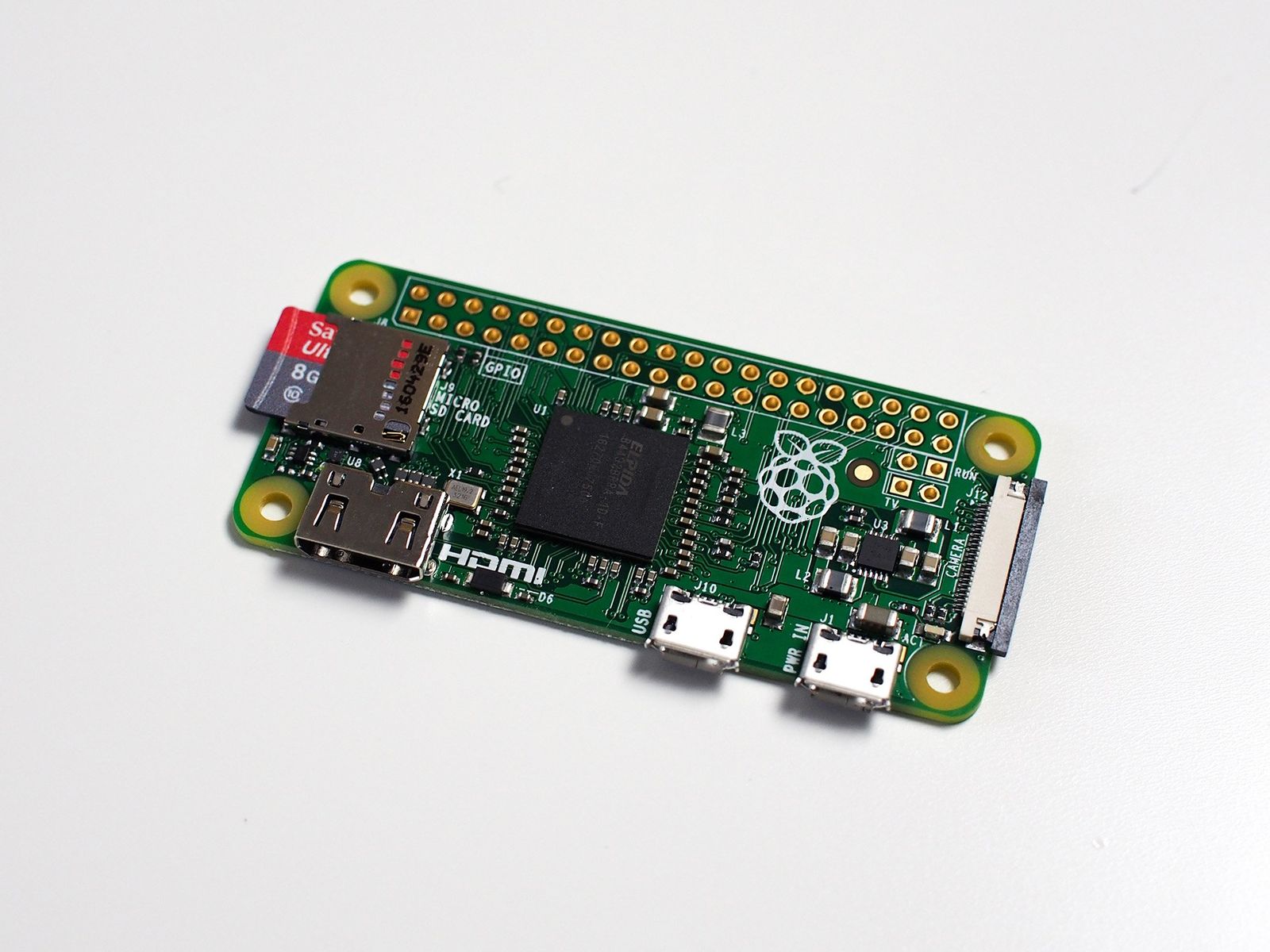
Preparing the Raspberry Pi Hardware
First things first, you'll want to gather your Raspberry Pi board, a good quality power supply, and a microSD card. The microSD card is where your operating system will live, so picking one that's reliable and has enough space is a good idea. You'll also need a monitor, keyboard, and mouse for the initial setup, just for a little while, anyway.
Once you have your parts, put the microSD card into the Pi's slot. Connect the monitor, keyboard, and mouse. Then, plug in the power supply. The Pi should light up and begin its boot process. This initial physical connection is pretty much the only time you'll need it if your remote setup goes well, you know.
Getting Started with Raspberry Pi OS
For most remote IoT projects, Raspberry Pi OS (formerly Raspbian) is the go-to operating system. It’s built specifically for the Pi and offers a lot of tools that are helpful for remote access. You can download the image from the official Raspberry Pi website and use a tool like Raspberry Pi Imager to put it onto your microSD card. This process is quite simple, actually.
After the operating system is installed and your Pi boots up, you'll go through a quick setup wizard. This is where you set your country, language, and create a user account. It's also a good time to connect your Pi to your Wi-Fi network. Making sure your Pi is connected to the internet is, you know, absolutely essential for remote access.
One very important step for remote access is to enable SSH. This is typically done through the Raspberry Pi Configuration tool under the "Interfaces" tab. Just tick the box next to SSH, and you're pretty much good to go on that front. Without SSH enabled, you won't be able to connect securely from another computer, so that's a crucial thing to remember, apparently.
Understanding VPC and Its Role in Secure Remote IoT
When you're dealing with remote devices, especially those handling important data or controlling things in your home, security is a big concern. This is where concepts like Virtual Private Clouds (VPCs) come into play. They help create a safe space for your devices to communicate, which is really quite important, you know.
What is a Virtual Private Cloud (VPC)?
A Virtual Private Cloud, or VPC, is essentially a private network that exists within a larger public cloud environment. Think of it like having your own dedicated, fenced-off area inside a very large shared park. You get all the benefits of the park's resources, but your space is separate and protected from others. This separation provides a lot of control over your network settings, including IP addresses, subnets, and routing tables, so.
For remote IoT, a VPC can provide a secure and isolated network for your Raspberry Pi and other devices. This means your devices aren't directly exposed to the open internet, which significantly reduces the risk of unwanted access. You can set up specific rules, like firewalls, to control exactly what kind of traffic can come in or go out of your private network. It's a bit like having a very strict bouncer at the door, basically.
Building a Secure Bridge with SSH
SSH, or Secure Shell, is a network protocol that allows you to connect to a remote computer securely. It's like having a secure, encrypted tunnel through which you can send commands and receive information. For your Raspberry Pi, SSH is the primary way you'll interact with it from a distance, giving you a command-line interface as if you were sitting right in front of it. This is really quite handy, honestly.
When combined with a VPC, SSH creates a very strong security setup. Your Raspberry Pi sits safely inside your private cloud network, and you use SSH to establish a secure connection to it from your local computer. This means all your communication is encrypted, keeping your commands and any sensitive data private. It's a pretty standard and very reliable way to manage remote Linux-based systems, you know, and the Pi is no exception.
Using SSH also allows for more than just sending commands. You can transfer files, set up port forwarding, and even run graphical applications remotely, though that last one might be a bit slow on a Pi. The main point is that SSH provides a robust and flexible way to manage your remote IoT devices, offering a lot of control and peace of mind, too it's almost.
Connecting to Your Raspberry Pi via SSH
Once your Raspberry Pi is set up and SSH is enabled, connecting to it from another computer is the next logical step. This process is fairly straightforward, especially if you're using a computer with a Linux or macOS operating system. Windows users have great options too, as a matter of fact.
SSH Basics for Remote Pi Control
To connect via SSH, you'll need the IP address of your Raspberry Pi and the username and password you set up during the OS installation. On a Linux or macOS computer, you simply open a terminal and type `ssh username@pi_ip_address`. For example, it might look like `ssh pi@192.168.1.100`. You'll then be prompted for your password. It's pretty simple, actually.
For Windows users, a popular tool is PuTTY. You can download PuTTY, enter your Pi's IP address and the SSH port (which is usually 22), and then click "Open." A terminal window will appear, asking for your username and password. It’s a very reliable piece of software that a lot of people use for this kind of thing, you know.
Once you're connected, you'll see a command prompt for your Raspberry Pi. From here, you can run any command you would normally run if you were directly connected to the Pi with a keyboard and monitor. This includes updating software, checking sensor readings, or starting programs. It’s really quite powerful, this remote access, you know.
Tips for SSH Security
While SSH is secure by default, there are ways to make it even more robust. One of the best practices is to use SSH keys instead of passwords. SSH keys involve a pair of cryptographic keys: a public key that goes on your Raspberry Pi and a private key that stays on your local computer. This method is much more secure than using just a password, as it's nearly impossible to guess a key, arguably.
Another good tip is to change the default SSH port (22) to something else. This doesn't make it truly more secure, but it does reduce the number of automated scanning attempts from bots looking for open SSH ports. It's a simple change that can cut down on unwanted attention, basically.
Also, consider disabling password authentication entirely once you have SSH keys set up. This means only users with the correct private key can connect, making it much harder for someone to brute-force their way in. These steps, taken together, really do help keep your remote IoT setup safe, so.
The Windows 10 Question: Raspberry Pi and Microsoft's OS
Many people, when thinking about remote access and their Raspberry Pi, wonder if they can simply "download Windows 10" and run it on the device. This is a very common question, but the answer is a bit more nuanced than a simple yes or no. It's important to understand the different versions of Windows and their compatibility with the Pi's hardware, you know.
Windows 10 IoT Core: A Different Story
Yes, there is a version of Windows 10 that runs on the Raspberry Pi, but it's called Windows 10 IoT Core. This is not the full desktop version of Windows 10 that you use on your PC for browsing the web or running productivity software. Instead, Windows 10 IoT Core is a stripped-down operating system designed specifically for small, embedded devices like the Raspberry Pi. It's meant for running a single, dedicated application, usually for IoT projects, you know, rather than being a general-purpose desktop.
With Windows 10 IoT Core, you typically interact with the device remotely or through a web interface, not a traditional desktop environment. It’s a good choice for specific industrial or smart home applications where you need the familiarity of Windows development tools, but it won't give you the typical Windows desktop experience you might be expecting. It’s a bit like having a very specialized tool for a very specific job, you know.
Running Full Windows 10: The Realities
Trying to run the full desktop version of Windows 10, the one you use on your laptop or home computer, on a Raspberry Pi is generally not feasible for practical use. The Raspberry Pi uses an ARM-based processor, which is different from the x86 or x64 processors found in most desktop PCs. While there have been experimental projects to get Windows 10 ARM running on certain Raspberry Pi models, these are often very slow, lack proper driver support, and are not officially supported by Microsoft. It's a bit like trying to fit a square peg in a round hole, you know.
Even if you manage to get it to boot, the performance would be very poor, making it frustrating to use for anything beyond basic tasks. You might experience frequent slowdowns, applications crashing, or even the system becoming unresponsive. It's similar to how some people experience issues with applications on their regular Windows 10 computers, like a streaming app not opening or showing a blue screen error, only perhaps even more pronounced due to hardware limitations. For instance, just like when your Netflix app might not open on your Windows 10 PC due to compatibility problems, trying to force a complex OS onto hardware it wasn't designed for can lead to a whole host of similar frustrations, actually. It's simply not what the Raspberry Pi was built for, you know, when it comes to a full desktop operating system.
Alternative Approaches for Windows Users
If you're a Windows user and want to work with your Raspberry Pi, the best approach is to stick with Raspberry Pi OS on the Pi itself and use Windows tools to connect to it. As mentioned, PuTTY is excellent for SSH connections. For graphical remote access, you can install a VNC server on your Raspberry Pi and a VNC client on your Windows machine. This allows you to see the Raspberry Pi's desktop remotely, giving you a visual interface. This is a very common and effective way to manage your Pi from a Windows computer, you know.
You can also use tools like WinSCP for secure file transfers between your Windows PC and your Raspberry Pi. This makes it easy to move scripts, data, or configuration files back and forth. So, while you might not be running Windows 10 *on* the Pi, you can certainly use Windows 10 *to manage* your Pi very effectively. It's about using the right tool for the job, basically.
Practical Steps for a Remote IoT Setup
Setting up a robust remote IoT system involves more than just enabling SSH. You need to think about how your devices communicate over the network and how to keep things running smoothly over time. These steps will help make your remote IoT project more reliable, you know.
Network Configuration Considerations
For truly remote access, your Raspberry Pi needs a way to be reached from outside your local network. This often involves configuring your home router to forward specific ports to your Pi's IP address. This is called port forwarding. It tells your router that when someone tries to connect to a certain port from the internet, that traffic should be sent to your Raspberry Pi. It’s a very common step for remote access, actually.
However, port forwarding can introduce security risks if not done carefully. A more secure method, especially for sensitive projects, is to use a VPN (Virtual Private Network) or a cloud-based solution that creates a secure tunnel to your Raspberry Pi without directly exposing it to the internet. Services that help you manage devices within a VPC often provide these secure tunneling options, offering a safer way to reach your devices. This is often preferred for more serious setups, you know.
Another important network consideration is making sure your Raspberry Pi has a static IP address on your local network. If its IP address changes frequently, your remote connection attempts might fail. You can usually configure this in your router's settings or directly on the Raspberry Pi itself. This small step can save you a lot of headaches later on, honestly.
Automating Remote Tasks
Once you have remote access established, you can start automating tasks on your Raspberry Pi. This might involve scheduling scripts to run at certain times, collecting data automatically, or even triggering actions based on sensor readings. Tools like cron on Raspberry Pi OS allow you to schedule commands to run periodically, which is very useful for unattended operations. It's a pretty powerful feature, you know.
For more complex automation, you might consider using programming languages like Python. Python is very popular on the Raspberry Pi and has libraries for almost anything you can imagine, from controlling hardware to sending data to cloud services. You can write your scripts on your Windows 10 PC, then transfer them to your Pi using SSH or a tool like WinSCP, and then run them remotely. This makes development quite flexible, you know.
Setting up your Raspberry Pi to automatically start certain programs or services when it boots up is also a good idea for remote IoT. This ensures that even if the power goes out and comes back on, your device will resume its functions without needing manual intervention. It’s about making your system as self-sufficient as possible, which is really quite handy for remote deployments, more or less.
Troubleshooting Common Remote Access Issues
Even with careful setup, you might run into a few bumps along the way when trying to access your Raspberry Pi remotely. Don't worry, many common issues have simple fixes. It’s usually just a matter of checking a few things, you know.
If you can't connect via SSH, first check if your Raspberry Pi is powered on and connected to the network. Sometimes a simple reboot of the Pi or your router can fix connectivity problems. Also, double-check the IP address of your Pi; it might have changed if you don't have a static IP set up. This is a very common oversight, actually.
Another common issue is incorrect firewall settings, either on your Raspberry Pi, your router, or even your local computer. Make sure that SSH traffic (usually on port 22) is allowed to pass through. If you changed the default SSH port, make sure you're trying to connect to the correct new port. These network settings can be a bit tricky, but they're often the source of connection problems, you know.
Sometimes, the issue might be with your SSH client or credentials. Make sure you're using the correct username and password, or that your SSH keys are properly configured and have the right permissions. If you're getting "permission denied" errors, it's often related to these details. It’s worth going through your setup steps again, just to be sure, basically.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can I install full Windows 10 on a Raspberry Pi?
No, you generally cannot install the full desktop version of Windows 10 on a Raspberry Pi for practical use. The Raspberry Pi uses an ARM processor, which is not natively compatible with the standard Windows 10 designed for x86/x64 computers. While experimental projects exist, they often result in very poor performance and lack proper driver support. The official Microsoft operating system for Raspberry Pi is Windows 10 IoT Core, which is a stripped-down version for embedded applications, you know, not a full desktop replacement.
How do I securely access my Raspberry Pi remotely?
The most common and secure way to access your Raspberry Pi remotely is by using SSH (Secure Shell). SSH encrypts your connection, keeping your commands and data private. For enhanced security, you should use SSH keys instead of passwords and consider running your Raspberry Pi within a Virtual Private Cloud (VPC) environment. This helps isolate your device from the open internet, providing an extra layer of protection, you know. Learn more about remote access for Raspberry Pi.
What is the best way to manage IoT devices in a VPC?
Managing IoT devices like Raspberry Pis within a VPC typically involves using SSH for command-line control and potentially VNC for graphical access. Cloud providers offer tools to set up your VPC, configure network rules, and establish secure connections to your devices. This setup allows you to control access very precisely and monitor your devices securely. It's a very robust way to handle multiple IoT devices, especially in a professional setting, you know. Learn more about secure IoT practices on our site, and link to this page here.