Have you ever thought about controlling your devices from a distance? It's a pretty cool idea, right? When we talk about the internet of things, or IoT, it means connecting everyday objects to the internet. This lets them talk to each other and to us. Getting your Raspberry Pi, a tiny computer, to do its job from far away can make things much easier. It's about being able to see what your Pi is doing, change settings, or fix things without having to be right next to it. This kind of remote access is very useful for anyone working with smart gadgets or systems. You might be wondering how to get started with something like VNC on your Raspberry Pi for your IoT projects, no matter where you are, north, east, west, or south.
People are always looking for ways to make their technology work better for them. The idea of managing devices that are not physically near you is very appealing. For those who play around with Raspberry Pi, whether for home automation or more complex setups, having a clear way to connect remotely is a big plus. This guide will walk you through the steps, focusing on how to use VNC for your Raspberry Pi. It's a practical way to keep tabs on your projects and make sure everything runs smoothly.
This article is here to help you get a good grasp on setting up remote access. We will go over what IoT means, why remote control is such a good idea for your Raspberry Pi, and how to download and set up VNC. We'll also touch on some important things to think about when you are connecting from a distance. So, too it's almost like having your Pi right there with you, even when you're miles away. Let's explore how to make your IoT dreams a bit more real.
Table of Contents
- What is IoT, Anyway?
- Why Remote Access Matters for Your IoT Projects
- Getting Started with Raspberry Pi and VNC
- Preparing Your Raspberry Pi
- Downloading and Installing VNC on Raspberry Pi
- Connecting Remotely from Anywhere
- Common Questions About IoT Remote VNC Raspberry Pi
- Final Thoughts and Next Steps
What is IoT, Anyway?
The Internet of Things, or IoT, describes devices with sensors, processing ability, software, and other technologies that connect and exchange data with other devices and systems over the internet. This is what my text says, and it's a good way to put it. It refers to a network of physical devices, vehicles, appliances, and other physical objects that are embedded with sensors, software, and network. The term IoT, or internet of things, refers to the collective network of connected devices and the technology that facilitates communication between devices and the cloud, as well as between. This is all about things talking to each other, you know?
The internet of things, or IoT, is a network of interrelated devices that connect and exchange data with other IoT devices and the cloud. IoT devices are typically embedded with. The internet of things (IoT) is a network of physical devices that can transfer data to one another without human intervention. The term was first coined by a computer scientist. This means your smart thermostat, your connected car, or even a sensor in a factory could be part of this huge network. It's really quite a big idea.
The internet of things (IoT) refers to physical objects embedded with sensors that communicate with computers. The IoT enables the physical world to be digitally monitored or. The internet of things (IoT) consists of the internet protocol (IP) and transmission control protocol (TCP), which together provide the standards and rules for devices to connect. It connects ordinary objects to other objects or applications in the cloud, making them smart—intelligent and interactive. In simple terms, the internet of things (IoT) refers to the digitally connected universe of smart devices. These devices are embedded with internet connectivity, sensors, and other hardware. So, that's what we are talking about when we say IoT, basically.
Why Remote Access Matters for Your IoT Projects
Having the ability to reach your devices from a distance is a pretty big deal for IoT projects. Think about it. You might have a Raspberry Pi set up in a garden shed, monitoring plants, or perhaps in a far-off part of your house controlling lights. Going to that spot every time you need to check something or make a change can be a real hassle. Remote access changes all of that. It lets you do things from your couch, or even from a different city, which is quite convenient, honestly.
It's about convenience, yes, but also about efficiency. When you are working on several projects, or if your devices are spread out, remote access saves a lot of time and effort. You can make adjustments, gather data, or troubleshoot issues without having to physically interact with each device. This means you can manage more things with less fuss. It's a way to keep your projects moving forward, even when you are not right there.
Staying Connected
Being able to stay connected to your Raspberry Pi, no matter where it is, means you are always in the loop. You can check sensor readings, see if a process is running, or verify that your system is online. This constant connection helps you monitor the health and performance of your IoT setup. It's like having an eye on everything, all the time. This is very helpful for maintaining continuous operation.
For instance, if you have a weather station running on a Raspberry Pi in your backyard, you might want to see the latest temperature readings. With remote access, you just open an app on your phone or computer. You don't need to walk outside. This kind of immediate access to information is quite valuable, you know.
Managing Devices
Remote access makes managing your Raspberry Pi devices a lot simpler. You can install software updates, change configurations, or even restart your Pi from a distance. This is especially good if you have many devices deployed. Updating them manually would take a very long time. With remote control, you can handle multiple devices from one central spot. This really streamlines your work.
Imagine you have a fleet of Raspberry Pis controlling different parts of a smart farm. When it's time to update their software, you can do it all from your office. This saves you from having to visit each Pi individually, which is a big time-saver, apparently. It's a much more efficient way to keep your systems current.
Troubleshooting
When something goes wrong, remote access becomes absolutely essential. If your IoT device stops working as expected, you can connect to your Raspberry Pi to see error messages, check logs, or try to fix the problem. You might find that a simple command can get things running again. This saves you a trip to the device's location. It's a quick way to get things back on track.
For example, if a sensor connected to your Pi stops sending data, you can log in remotely to see if the sensor's software needs a restart or if there's a network issue. You can run diagnostic tools right from your computer. This capability means less downtime for your IoT projects, which is very important for continuous operation, really.
Getting Started with Raspberry Pi and VNC
To get started with remote control, you need a Raspberry Pi and a tool called VNC. These two work together to give you a graphical view of your Pi's desktop from another computer. It's like you're sitting right in front of your Pi, even if you are not. This combination is a popular choice for many people, and for good reason.
Understanding what each part does will help you set things up correctly. The Raspberry Pi is your little computer, and VNC is the software that lets you see and control its screen remotely. When you put them together, you get a powerful setup for managing your IoT projects from anywhere. It's a pretty straightforward process once you know the steps.
What is Raspberry Pi?
A Raspberry Pi is a small, single-board computer. It's about the size of a credit card, but it can do many things a regular desktop computer can do. People use them for all sorts of projects, from learning to code to building robots or smart home devices. They are very versatile and affordable. This makes them a favorite for hobbyists and professionals alike, you know.
It runs a version of Linux, typically Raspberry Pi OS. This operating system gives you a desktop environment, just like Windows or macOS, but it's lighter. You can connect a monitor, keyboard, and mouse to it, but for IoT projects, they often run without these, which is called a "headless" setup. That's where remote access comes in handy, obviously.
What is VNC?
VNC stands for Virtual Network Computing. It's a system that lets you view and interact with a computer's desktop from another computer over a network. Think of it as a remote desktop tool. When you use VNC, you see the screen of the remote computer on your local screen, and your mouse and keyboard inputs are sent to the remote computer. It's a direct way to control another machine.
There are different VNC software options available, but they all work on the same basic principle. One computer acts as the "server," sharing its screen, and another acts as the "client," viewing and controlling it. For our purposes, your Raspberry Pi will be the VNC server. This setup allows for a graphical interface, which is very user-friendly, as a matter of fact.
Why VNC for Raspberry Pi IoT?
VNC is a good choice for Raspberry Pi IoT projects because it provides a full graphical interface. Sometimes, you need to see what's happening on the screen, like when you are debugging a graphical application or configuring a sensor that has a visual setup tool. Command-line access is fine for many tasks, but VNC gives you the whole picture. It's more intuitive for some operations, honestly.
It's also pretty easy to set up on Raspberry Pi OS, which comes with VNC Server pre-installed or readily available. This makes the process simpler for users. The visual feedback you get from VNC can make troubleshooting much quicker, especially for those who are more comfortable with a desktop environment. So, it's a very practical solution for many situations, you know.
Preparing Your Raspberry Pi
Before you can get VNC up and running, your Raspberry Pi needs a little preparation. This involves making sure it has the right operating system and that it's connected to a network. These are foundational steps that will make the rest of the process much smoother. It's like getting your tools ready before you start a project, basically.
Having a well-prepared Pi means less frustration later on. A stable operating system and a reliable network connection are key to successful remote access. Take a few moments to ensure these basics are covered. It will save you time and effort in the long run, seriously.
Setting Up Your Pi
First, you need to have Raspberry Pi OS installed on your Pi's microSD card. If you haven't done this yet, you can use the Raspberry Pi Imager tool to flash the operating system onto the card. It's a straightforward process. Make sure you choose the desktop version of Raspberry Pi OS, as VNC works best with a graphical environment. This will give you the visual interface you need.
Once the OS is installed, boot up your Raspberry Pi. You might need a monitor, keyboard, and mouse for this initial setup. Make sure the system is fully updated by opening a terminal and running `sudo apt update` followed by `sudo apt upgrade`. This keeps your software current. It's a good habit to update regularly, you know.
Network Connections
Your Raspberry Pi needs to be connected to a network so you can access it remotely. This can be via Wi-Fi or an Ethernet cable. For most IoT projects, a Wi-Fi connection is common because it offers flexibility in placement. Make sure your Pi is connected to the same network as the computer you will use to access it remotely, at least initially. This simplifies the connection process.
To check your Pi's IP address, open a terminal and type `hostname -I`. This command will show you the IP address assigned to your Pi on the network. You will need this IP address later to connect with VNC. It's a good idea to write it down. A stable network connection is very important for uninterrupted remote access, after all.
Downloading and Installing VNC on Raspberry Pi
Now we get to the core of it: getting VNC onto your Raspberry Pi. The good news is that Raspberry Pi OS often comes with VNC Server pre-installed, or it's very easy to add. This means you might not even need to "download" anything new if your OS version is recent. You just need to enable it and set it up, which is pretty convenient.
If for some reason it's not there, adding it is simple using the command line. This section will guide you through activating VNC Server and making sure it's ready for connections. It's a key step for your remote control setup, obviously.
Step-by-Step Guide
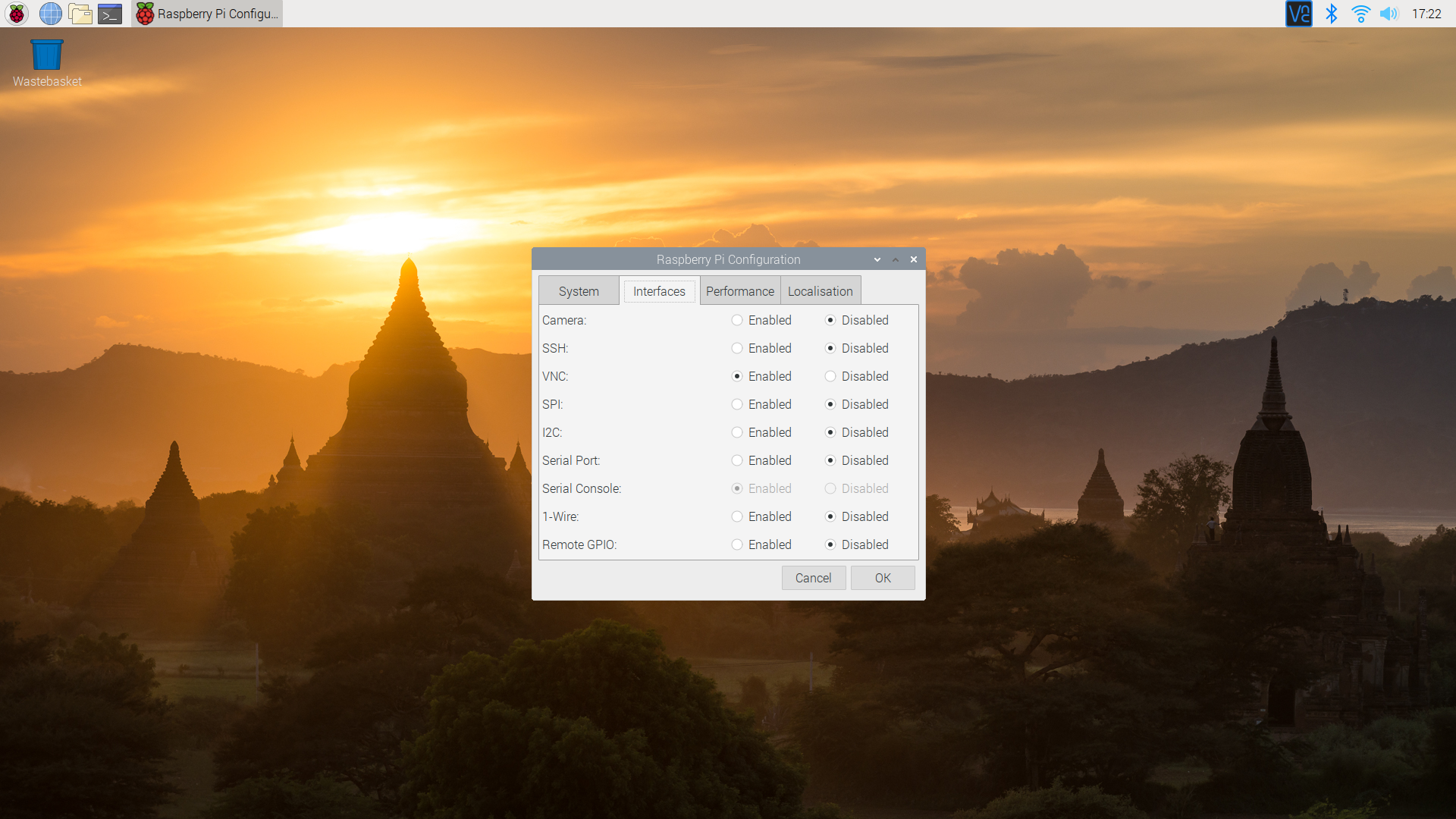
First, open the Raspberry Pi Configuration tool. You can find this in the main menu under "Preferences." Once it's open, go to the "Interfaces" tab. Look for "VNC" and make sure it's enabled. If it's not, click the radio button to turn it on. This is the simplest way to get VNC Server running. It's a quick toggle, really.
If VNC Server is not pre-installed or if you prefer the command line, you can install it. Open a terminal and type: `sudo apt install realvnc-vnc-server`. Press Enter and let it complete the installation. This command will fetch and install the necessary files. It's a common way to add software on Linux systems, you know.
After enabling or installing VNC, you need to set a password for VNC connections. This is separate from your Pi's login password. When VNC Server starts, it will usually prompt you to set this up. If not, you can manage VNC settings from the VNC Server icon in your Pi's top right corner. Click the icon, go to "Options," then "Users & Permissions" to set a strong password. This is very important for security.
Configuration Tips
You can adjust some settings in VNC Server to make your remote experience better. For instance, you can change the resolution of the remote desktop. If your Pi is running headless (without a monitor), you might want to set a specific resolution so your VNC view looks good on your client device. You can do this in the VNC Server options under "Display." It's a way to tailor the experience.
Another tip is to configure VNC to start automatically when your Raspberry Pi boots up. This is usually the default behavior once enabled, but it's good to double-check. This means you won't have to manually start VNC Server every time your Pi restarts. It ensures your Pi is always ready for remote access, which is pretty convenient, you know.
Connecting Remotely from Anywhere
Once VNC Server is running on your Raspberry Pi, the next step is to connect to it from another device. This could be your laptop, desktop computer, or even a smartphone. You will need a VNC client application on the device you are connecting from. There are many free and paid VNC clients available for different operating systems. Choosing one that suits your needs is fairly easy.
The process involves entering your Raspberry Pi's IP address and the VNC password you set earlier. This establishes the connection and brings your Pi's desktop onto your screen. It's a straightforward way to bridge the distance between you and your IoT projects, you know.
Using a VNC Client
To connect, first download and install a VNC client on your local computer. Popular options include RealVNC Viewer, TightVNC, or Remmina (for Linux). Once installed, open the VNC client. It will usually ask for the IP address or hostname of the VNC server you want to connect to. Enter the IP address of your Raspberry Pi that you noted earlier. This is how the client knows where to look.
After entering the IP address, the client will prompt you for the VNC password. Type in the password you created for VNC Server on your Pi. Once authenticated, you should see the desktop of your Raspberry Pi appear on your screen. You can now control it as if you were sitting right in front of it. It's a pretty seamless experience, really.
Security Considerations
When you are accessing your Raspberry Pi remotely, security is very important. Always use a strong, unique password for your VNC connection. Avoid simple passwords that are easy to guess. This protects your Pi from unauthorized access. A weak password is like leaving your front door unlocked, you know.
If you plan to access your Pi from outside your home network, you should use a secure method. Directly opening ports on your router to expose VNC to the internet is generally not recommended due to security risks. Instead, consider using a Virtual Private Network (VPN) or an SSH tunnel. These methods create a secure, encrypted connection to your home network first, and then you connect to VNC over that secure tunnel. This adds a layer of protection, which is very wise, obviously. Learn more about VNC on Raspberry Pi on the RealVNC website.
Accessing Your Pi, North, East, West, or South
The beauty of remote access is that your physical location doesn't matter. Whether your Raspberry Pi is in a shed in the north, a factory in the east, a remote sensor array in the west, or a home automation hub in the south, VNC allows you to connect. The principles of setting up VNC and connecting to it remain the same, regardless of the compass direction. It's all about network connectivity.
What changes is how you establish that network connection from a distance. For local network access, it's simple. For remote access over the internet, you will rely on the secure methods mentioned, like VPNs or SSH tunnels. These tools make sure your connection is safe, no matter how far away you are. So, you can truly manage your IoT devices from virtually anywhere, which is very empowering, you know.
Common Questions About IoT Remote VNC Raspberry Pi
People often have similar questions when they are getting into remote access for their Raspberry Pi IoT projects. Here are a few common ones that might be on your mind.
Can I access my Raspberry Pi from my phone using VNC?
Yes, you absolutely can. There are VNC client applications available for both Android and iOS devices. You can download one from your phone's app store, enter your Raspberry Pi's IP address and VNC password, and you will see your Pi's desktop right on your phone screen. It's a very convenient way to manage your devices on the go, actually.
What if my Raspberry Pi's IP address changes?
IP addresses can sometimes change, especially if your router assigns them dynamically. If your Pi's IP address changes, your VNC client won't be able to connect using the old address. You will need to find the new IP address. One way to deal with this is to set a static IP address for your Raspberry Pi in your router settings. Another option is to use a dynamic DNS service, which assigns a hostname that always points to your Pi's current IP. This makes it much easier to connect consistently, you know.
Is VNC secure enough for sensitive IoT applications?
VNC itself provides encryption for its connections, which is good. However, for truly sensitive IoT applications, relying solely on VNC might not be enough, especially if you are connecting over the open internet. As mentioned earlier, it's highly recommended to use VNC over a secure tunnel like a VPN or SSH. This adds a layer of strong encryption and authentication, making your remote connection much safer. It's about building a robust security posture, obviously.
Final Thoughts and Next Steps
Setting up remote access for your Raspberry Pi using VNC opens up a world of possibilities for your IoT projects. It gives you the freedom to manage and monitor your devices from anywhere, which is a huge benefit for anyone building smart systems. From checking sensor data to making quick software changes, VNC makes it all much more accessible. It's a tool that really helps you keep control, no matter where your projects take you.
Remember to always keep security in mind when you are working with remote connections. Strong passwords and secure tunneling methods like VPNs are your best friends here. By following these steps, you can create a reliable and safe way to interact with your Raspberry Pi. So, go ahead and explore the potential of remote control for your IoT devices. It's a very rewarding experience, you know. You can also learn more about Raspberry Pi projects on our site, and for more specific guides, link to this page here.